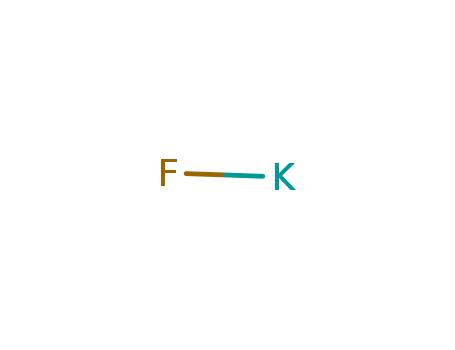
7789-23-3
- Product Name:Potassium fluoride
- Molecular Formula:KF
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:58.0967
Product Details
Manufacturers supply cost-effective and customizable Potassium fluoride 7789-23-3
- Molecular Formula:FK
- Molecular Weight:58.0967
- Appearance/Colour:white powder or crystals with a sharp saline taste
- Vapor Pressure:922mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:858 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.363
- Boiling Point:1505 °C
- Flash Point:1505°C
- PSA:0.00000
- Density:2.48 g/cm3
- LogP:-2.99600
Potassium fluoride(Cas 7789-23-3) Usage
|
Physical and Chemical Properties |
Potassium fluoride is basis raw material of manufacturing fluoride, chemical formula is KF. Molecular weight is 58.10. It is colorless cubic crystal or white powder. It is poisonous! It is deliquescent. Taste is salty. Specific gravity is 2.48. Melting point is 858℃. Boiling point is 1505℃. It is soluble in water. It was dissolved in hydrofluoric acid and ammonia. It is insoluble in ethanol, acetone. Aqueous solution is alkaline and it can corrode glass and porcelain. It can cause irritation for human skin, mucous membrane and eye. When belows 40.2℃, it can crystallize in an aqueous solution to give dihydrate KF·2H2O, which is monoclinic, it is self-dissolved crystalline water at 41℃. It can be obtained by the thermal decomposition of potassium hydrogen fluoride or potassium carbonate (or potassium hydroxide) and hydrofluoric acid (40% or anhydrous). It can be used for glass engraving, food preservation, it can be also used as welding flux, fluoride, pesticides,etc. Figure 1 the structural formula of potassium fluoride. |
|
Preparation |
Potassium fluoride is prepared by reacting potassium carbonate (or KOH) with aqueous hydrofluoric acid. Care is necessary in handling the anhydrous salt, to prevent its hydration. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Potassium fluoride reacts with acids to evolve corrosive and toxic hydrogen fluoride. Aqueous solutions corrode glass and consequently are prepared and stored in polyethylene containers. The pure solid may be stored in glass containers. Reacts violently with (Pt + BrF3). [NTP 1992]. |
|
Health Hazard |
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous route. Experimental teratogenic effects. A corrosive irritant to the eyes, skin, and mucous membranes. Mutation data reported. A very reactive material. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of K2O and F-. Used in etchmg glass, as a presewative, as an insecticide, and in organic synthesis. See also FLUORIDES and HYDROFLUORIC ACID. |
|
Potential Exposure |
Potassium fluoride is used in etching glass; as a preservative and insecticide. |
|
Shipping |
UN1812 Potassium fluoride, solid, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Incompatible with strong acids; reacts releasing hydrogen fluoride. Aqueous solutions corrode glass and consequently are prepared and stored in polyeth- ylene containers. The pure solid may be stored in glass containers. Reacts violently with (Pt 1 BrF 3 ) |
InChI:InChI=1/FH.K/h1H;/q;+1/p-1
7789-23-3 Relevant articles
Investigation of KYF4: Yb, Er // KYF4 nanocrystals - Mechanism of the KYF4 formation
Sch?fer,Ptacek,Hickmann,Prinz,Neumann,Haase
, p. 1914 - 1920 (2009)
This paper presents our investigation of...
Phase transitions in K3AlF6
Abakumov, Artem M.,Rossell, Marta D.,Alekseeva, Anastasiya M.,Vassiliev, Sergey Yu.,Mudrezova, Svetlana N.,Van Tendeloo, Gustaaf,Antipov, Evgeny V.
, p. 421 - 428 (2006)
Phase transitions in the elpasolite-type...
Two anhydrous salts of tetrafluoroterephthalic acid (H2tF-BDC): K2tF-BDC and Rb2tF-BDC
Werker, Melanie,Dolfus, Benedikt,Ruschewitz, Uwe
, p. 2487 - 2492 (2013)
Two new anhydrous salts of tetrafluorote...
Measurement of absolute rate data for the reaction of atomic potassium, K(4 2S1/2), with CF3Cl, CF2Cl2, CFCl3, CF3Br and SF6 as a function of temperature by time-resolved atomic resonance absorption spectroscopy at λ = 404 nm [k(5 2PJ) ← K(4 2S1/2)]
Husain, David,Lee, Yook Heng
, p. 2325 - 2337 (1987)
We present a kinetic study of the reacti...
Exploration on anion ordering, optical properties and electronic structure in K3WO3F3 elpasolite
Atuchin,Isaenko,Kesler,Lin,Molokeev,Yelisseyev,Zhurkov
, p. 159 - 164 (2012)
Room-temperature modification of potassi...
Wet chemical synthesis of LiBaF3 phosphor
Singh, Vartika S.,Joshi,Moharil
, p. 165 - 168 (2013)
LiBaF3 has great potential applications ...
The mild hydrothermal synthesis of complex fluorides of AZnF3 (A = Na, K)
Li, Hong,Jia, Zhihong,Shi, Chunshan
, p. 1106 - 1107 (2000)
The complex fluorides of AZnF3 (A = Na, ...
A novel 18F labelled imidazo-oxazolopyridine derivative as β-amyloid imaging agent: Synthesis and preliminary evaluation
Singh, Shivani,Singh, Sweta,Tiwari, Anjani Kumar,Sharma, Rakesh Kumar,Mathur, Rashi,Kaul, Ankur
, p. 183 - 190 (2018)
Visualization of β-amyloid plaques in br...
Molecular Beam Study of Steric Effects in the Reaction K + HF (v = 1, j = 2) -> KF + H
Hoffmeister, Manfred,Schleysing, Ruediger,Loesch, Hansjuergen
, p. 5441 - 5445 (1987)
HF molecules were optically aligned by u...
The crystal structure of α-K3AIF6: Elpasolites and double perovskites with broken corner-sharing connectivity of the octahedral framework
Abakumov, Artem M.,King, Graham,Laurinavichute, Veronika K.,Rozova, Marina G.,Woodward, Patrick M.,Antipov, Evgeny V.
, p. 9336 - 9344 (2009)
The crystal structure of α-K3AIF6 was so...
A metabolically stable PET tracer for imaging synaptic vesicle protein 2A: synthesis and preclinical characterization of [18F]SDM-16
Zheng, Chao,Holden, Daniel,Zheng, Ming-Qiang,Pracitto, Richard,Wilcox, Kyle C.,Lindemann, Marcel,Felchner, Zachary,Zhang, Li,Tong, Jie,Fowles, Krista,Finnema, Sjoerd J.,Nabulsi, Nabeel,Carson, Richard E.,Huang, Yiyun,Cai, Zhengxin
, p. 1482 - 1496 (2021/11/16)
Purpose: To quantify the synaptic vesicl...
NHC-Copper Mediated Ligand-Directed Radiofluorination of Aryl Halides
Sharninghausen, Liam S.,Brooks, Allen F.,Winton, Wade P.,Makaravage, Katarina J.,Scott, Peter J. H.,Sanford, Melanie S.
supporting information, p. 7362 - 7367 (2020/08/19)
[18F]-labeled aryl fluorides are widely ...
Compositions, methods, and systems for the synthesis and use of imaging agents
-
Page/Page column 92, (2016/08/17)
The present invention generally relates ...
7789-23-3 Process route
-

-
7558-02-3,7758-02-3
potassium bromide

-

-
7789-23-3
potassium fluoride
-
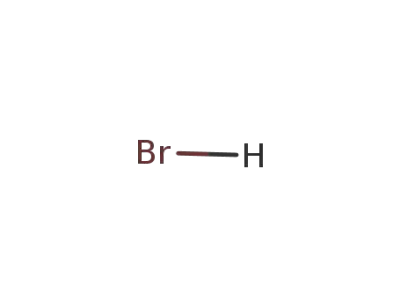
-
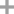
10035-10-6,12258-64-9
hydrogen bromide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogen fluoride;
during dissolving at 14-18 °C;
|
|
|
With
HF;
|
-
-
7782-41-4
fluorine

-

-
potassium hydroxide

-

-
7789-23-3
potassium fluoride

-
-
10028-15-6
ozone
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
melt;
reaction by use of molten KOH in a F2 atmosphere;; formation of a KF layer beside O3;;
|
|
|
In
melt;
reaction by use of molten KOH in a F2 atmosphere;; formation of a KF layer beside O3;;
|
7789-23-3 Upstream products
-
7664-39-3
hydrogen fluoride
-
7440-09-7
potassium
-
1310-58-3
potassium hydroxide
-
354-87-0
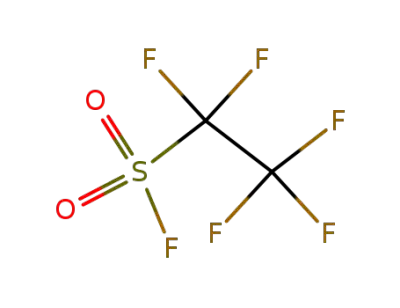
pentafluoroethanesulfonyl fluoride
7789-23-3 Downstream products
-
7789-24-4

lithium fluoride
-
7558-02-3

potassium bromide
-
7647-14-5

sodium chloride
-
13455-22-6
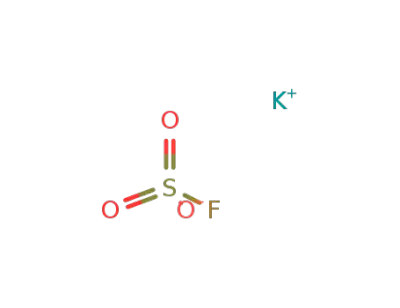
potassium fluorosulfonate
Relevant Products
-
Potassium hydrogen fluoride
CAS:7789-29-9
-
Ethanediammonium Diacetate
CAS:38734-69-9
-
2,4-Difluoropyridine
CAS:34941-90-7